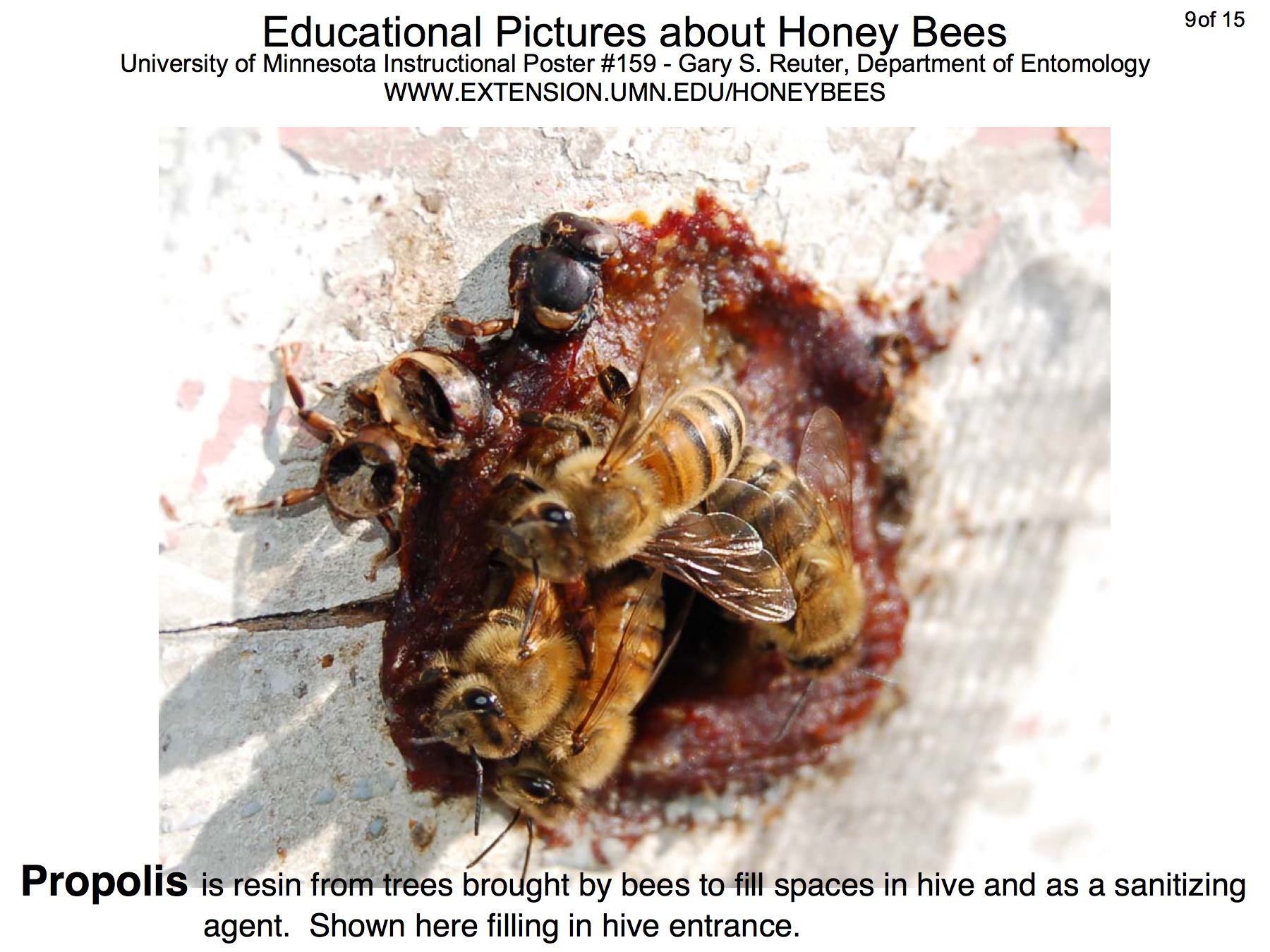
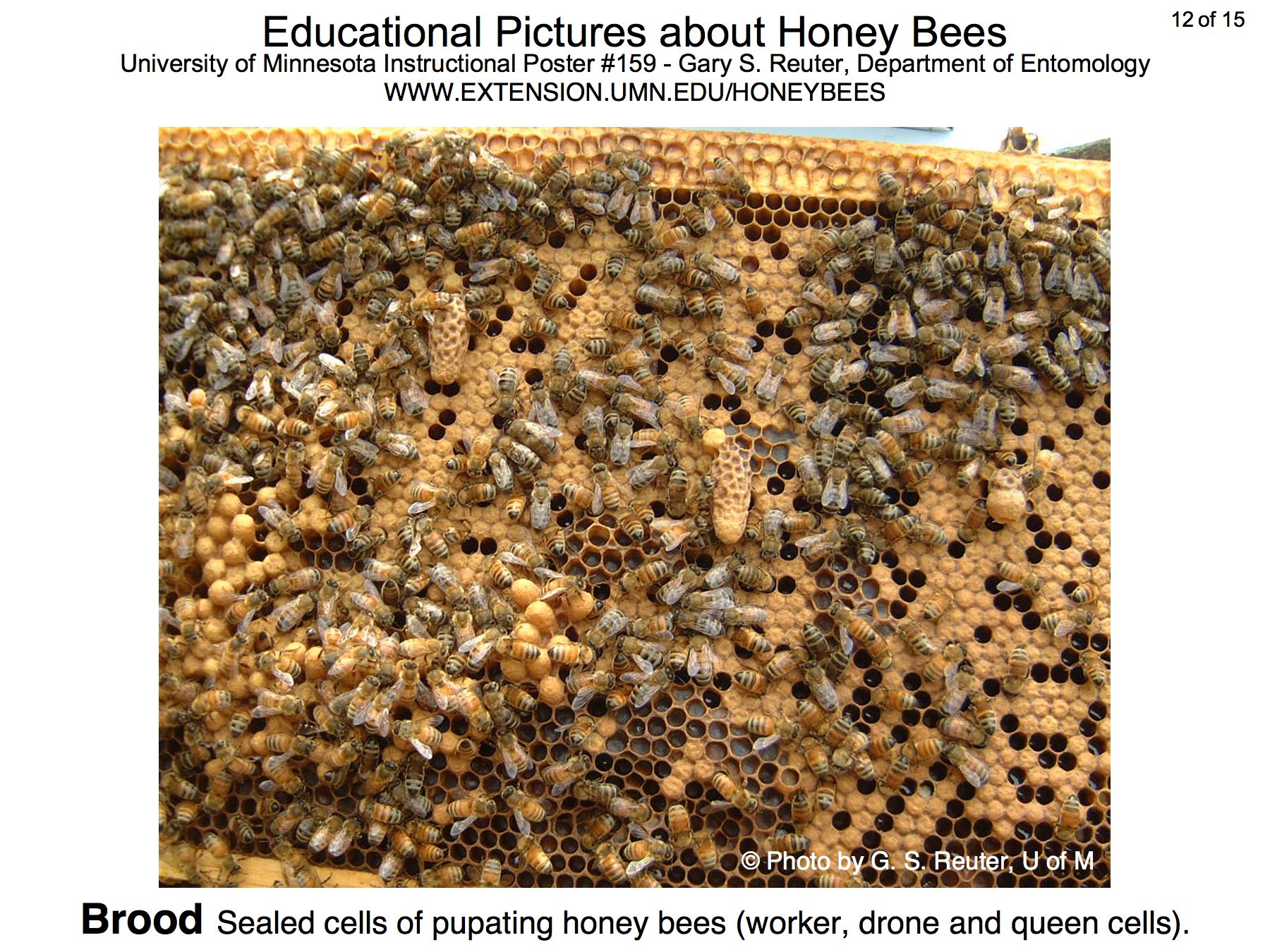
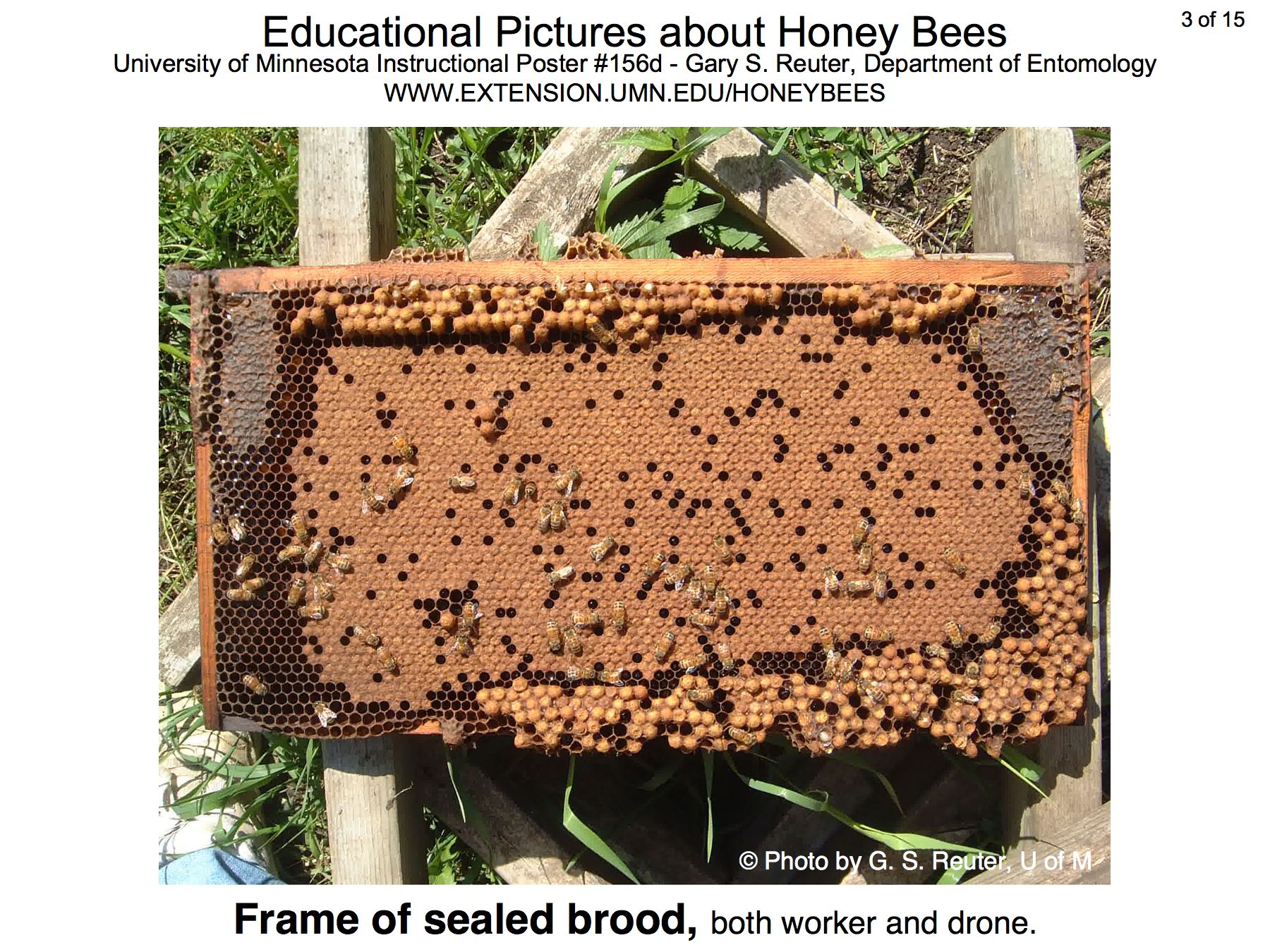
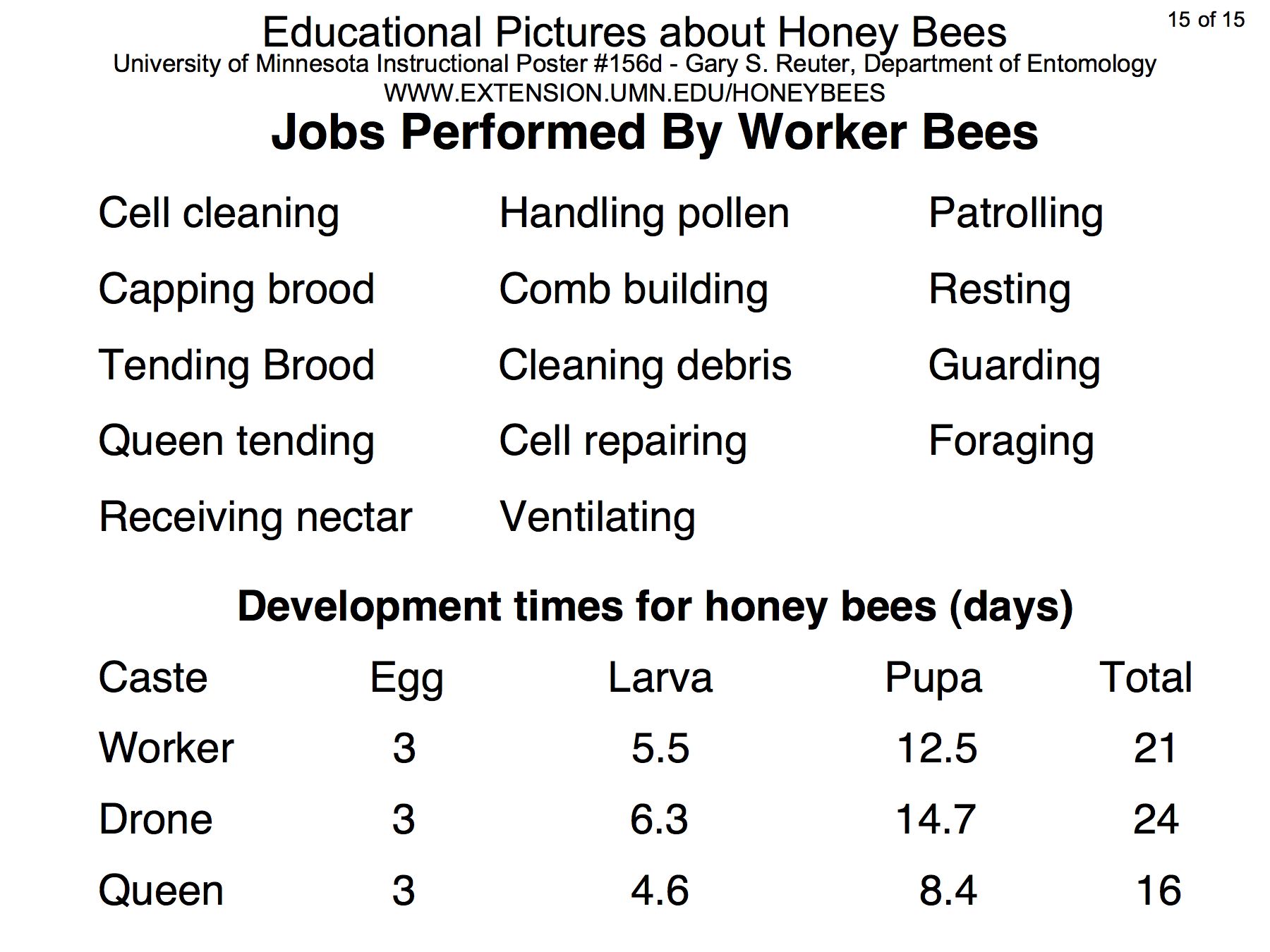
The poster above is available on the bee lab web site z.umn.edu/freebee. Copies of individual pictures (1800 x 1350 pixels) are available below.
The following pictures are 500 x 400 pixel copies (click picture to download) of the figures in Honey Bee Diseases and Pest manual 2016 by Marla Spivak and Gary Reuter. Information on the manual is available here.
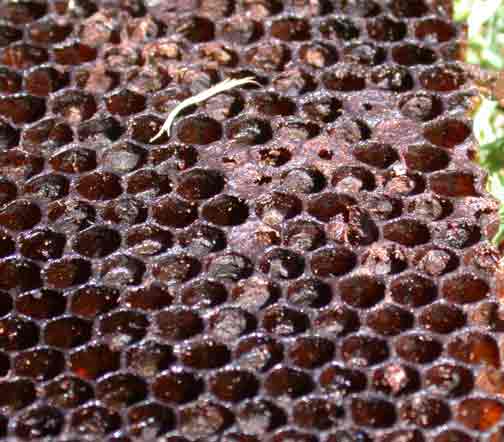
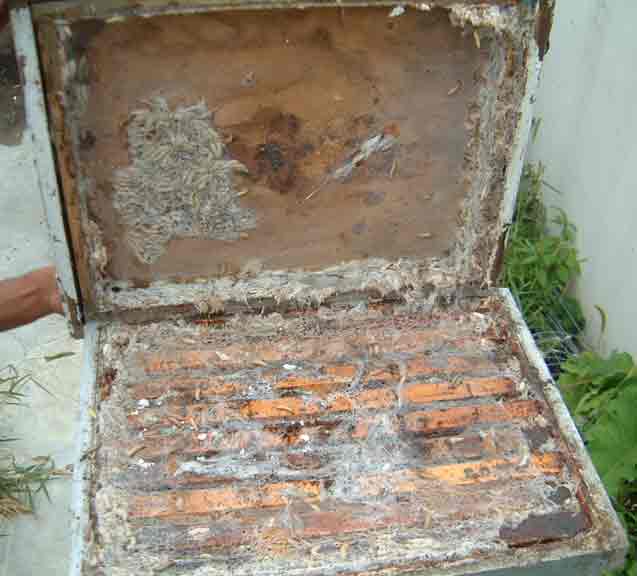
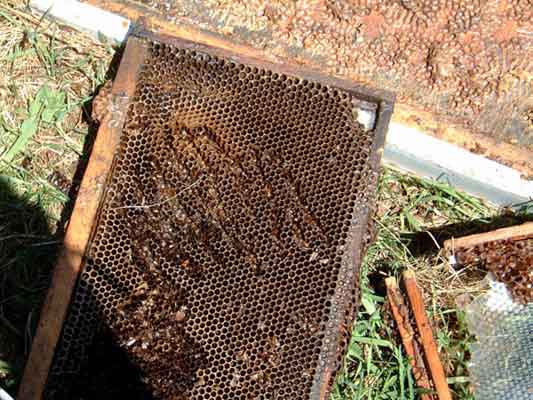
Figure 1. Old comb with AFB “scale” hardened and stuck to lower edge of comb. Comb is upside down in photo to expose lower part of cells.
Figure 2. AFB kills sealed brood. Symptoms include brood cells with perforated cappings and brown, gooey, smelly dead brood inside.
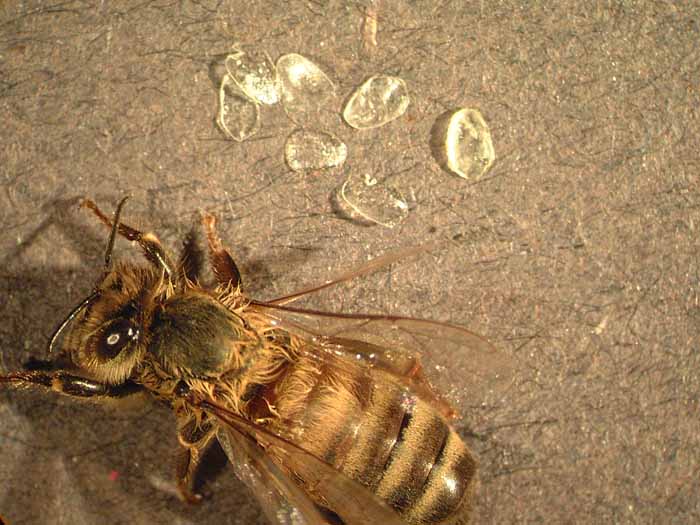
Figure 3. The “ropiness” test to determine if brood has AFB
Figure 4. An EFB infection kills larvae before they are sealed. The dead larvae do not become ropy.
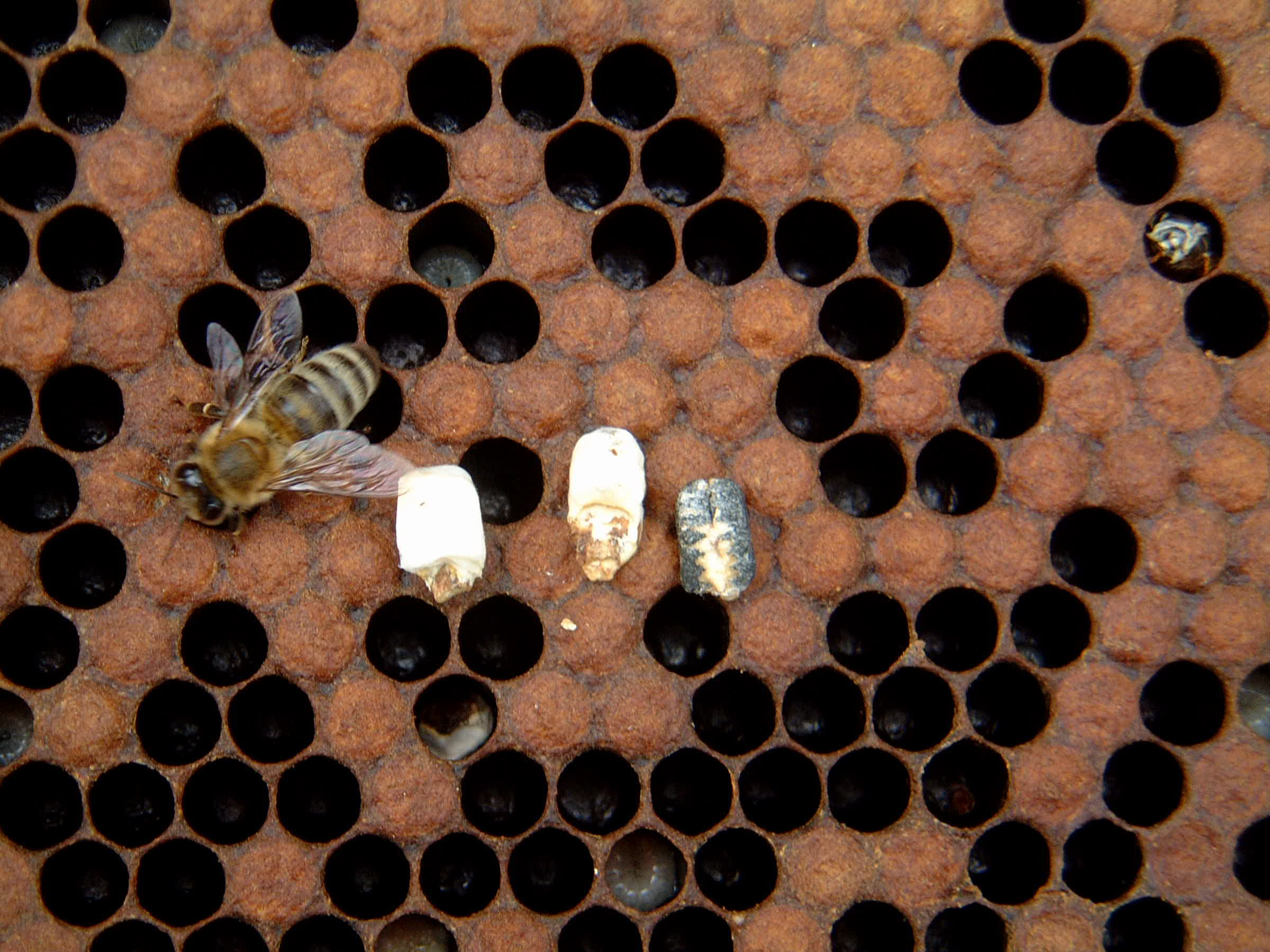
Figure 5. Chalkbrood kills sealed brood. Symptoms include brood cells with perforated or opened capping with hard white or black “mummies” inside.
Figure 6. Close-up of chalkbrood mummies.
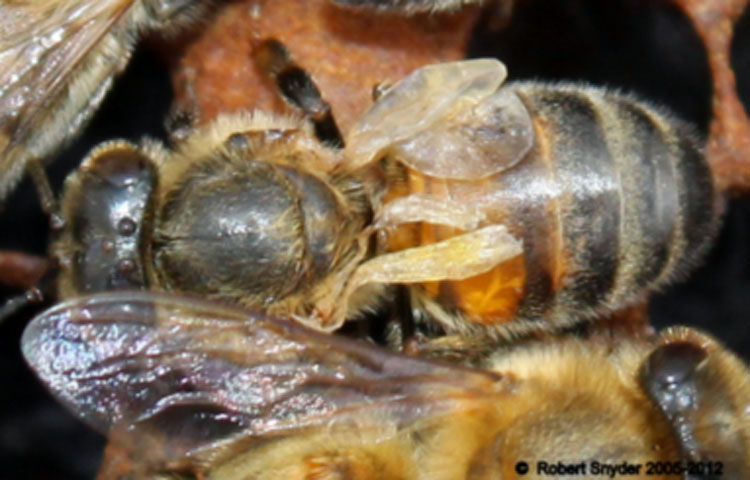
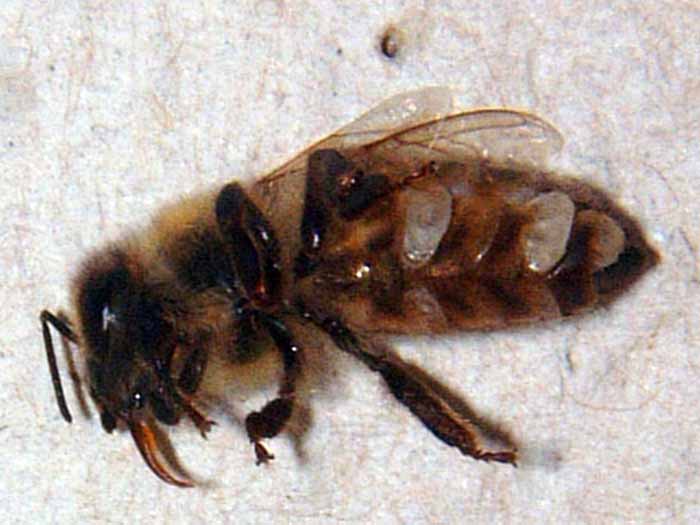
Figure 7. Close up of bee with deformed wing virus (DWV)
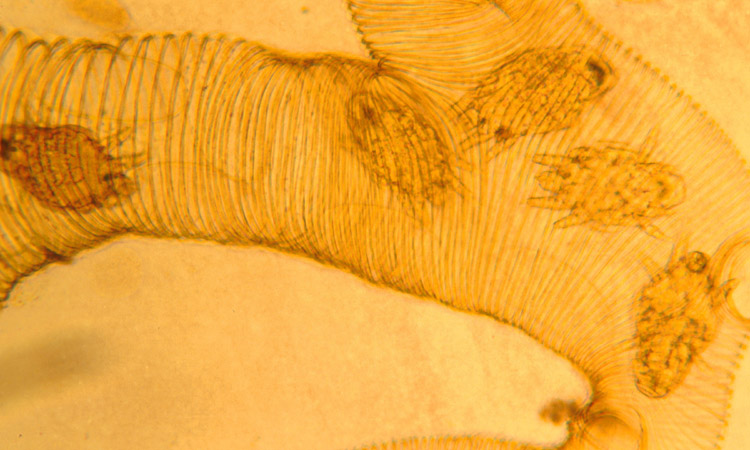
Figure 8. Tracheal mites in breathing tubes (trachea) of a bee, viewed through a microscope (100-200X).
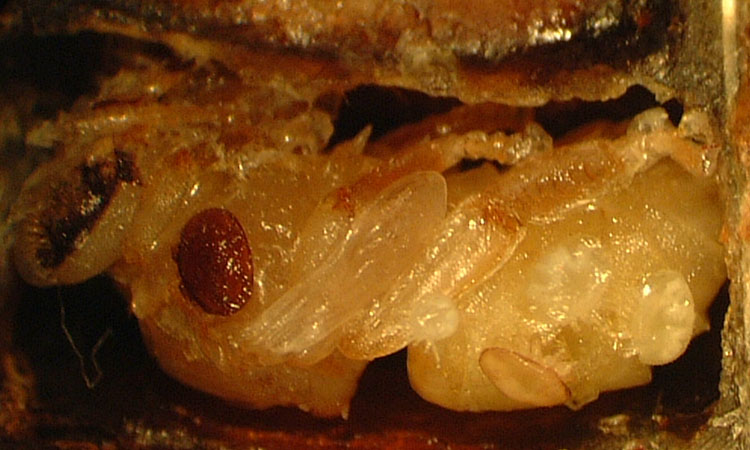
Figure 9. Varroa mites on a bee pupa (cell wall was removed for the photo).
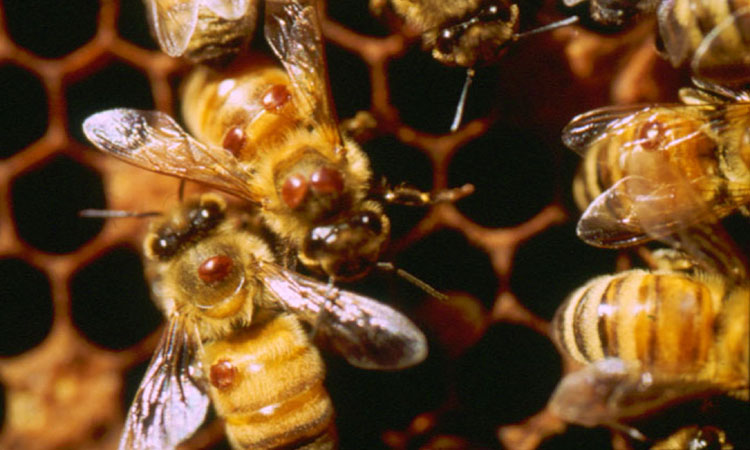
Figure 10. Varroa mites on thorax of adult bees.
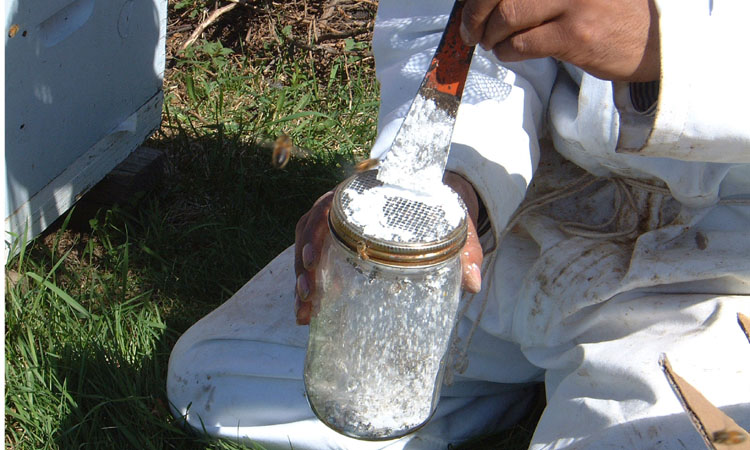
Figure 11. Powdered sugar method for sampling varroa showing the sugar being put into jar.
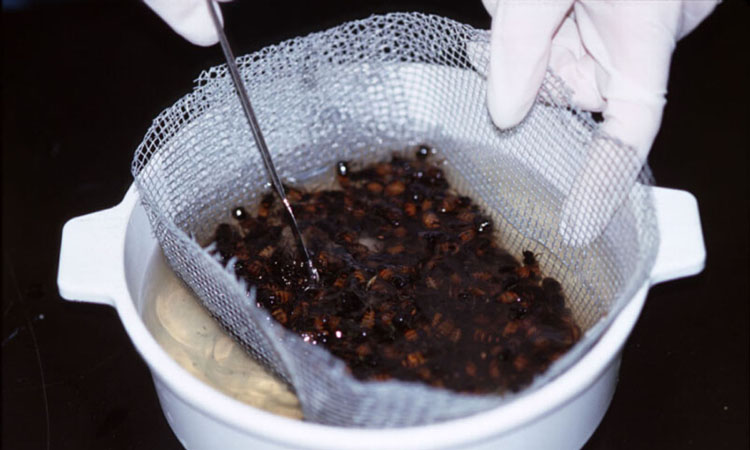
Figure 12. Alcohol wash showing screen full of bees.
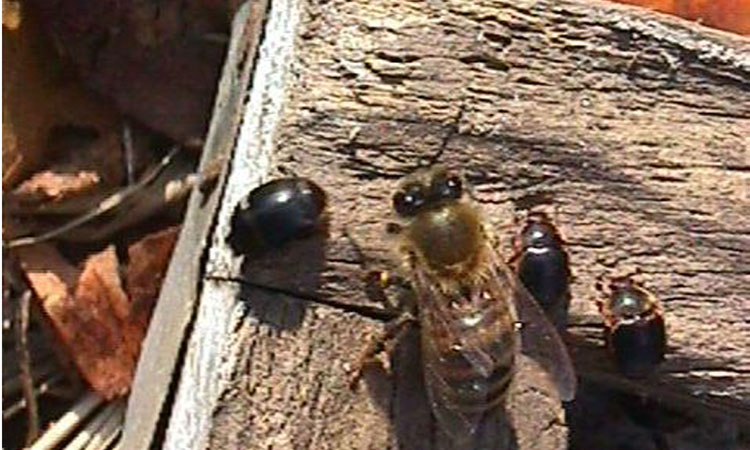
Figure 13. Mug shot of small hive beetles next to a honey bee.
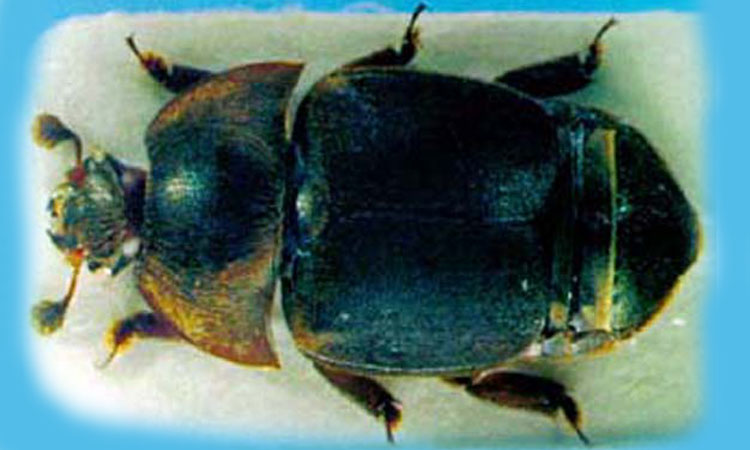
Figure 14. Close shot of small hive beetle. Note “clubbed” antennae.
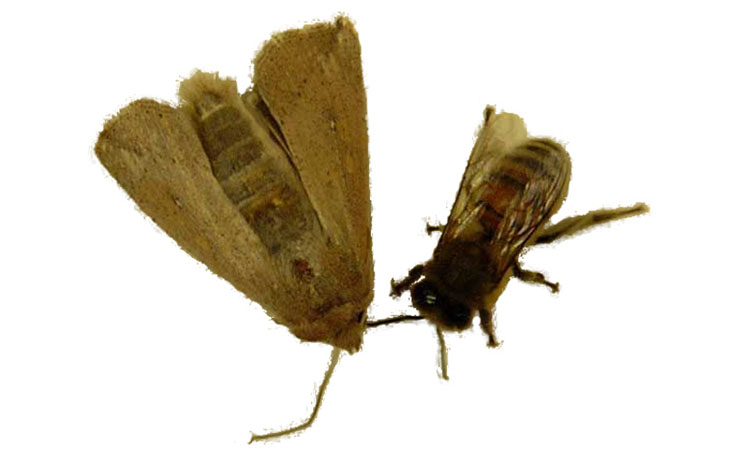
Figure 15. Mug shot of greater wax moth next to a honey bee.
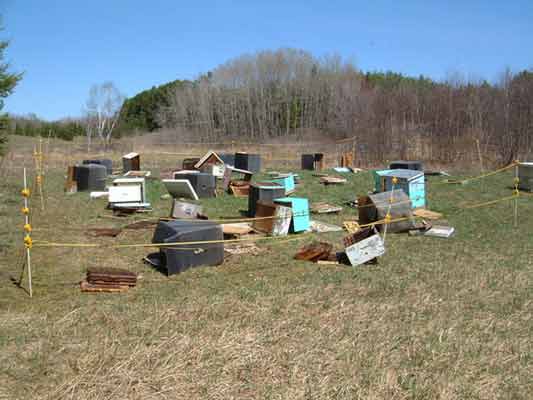
Figure 16. Electric fence around an apiary.